systole.plots.plot_frequency#
- systole.plots.plot_frequency(rr: Union[ndarray, list], input_type: str = 'peaks', fbands: Optional[Dict[str, Tuple[str, Tuple[float, float], str]]] = None, figsize: Optional[Union[int, List[int], Tuple[int, int]]] = None, backend: str = 'matplotlib', ax: Optional[Axes] = None, **kwargs) Union[figure, Axes][source]#
Plot power spectral densty of RR time series.
- Parameters
- rr
Boolean vector of peaks detection or RR intervals.
- input_type
The type of input vector. Default is “peaks” (a boolean vector where 1 represents the occurrence of R waves or systolic peaks). Can also be “rr_s” or “rr_ms” for vectors of RR intervals, or interbeat intervals (IBI), expressed in seconds or milliseconds (respectively).
- fbands
Dictionary containing the names of the frequency bands of interest (str), their range (tuples) and their color in the PSD plot. Default is:
{ 'vlf': ('Very low frequency', (0.003, 0.04), 'b'), 'lf': ('Low frequency', (0.04, 0.15), 'g'), 'hf': ('High frequency', (0.15, 0.4), 'r') }
- figsize
Figure size. Default is (13, 5).
- ax
Where to draw the plot. Default is None (create a new figure).
- backend
Select plotting backend (“matplotlib”, “bokeh”). Defaults to “matplotlib”.
- Returns
- plot
The matplotlib axes, or the boken figure containing the plot.
See also
plot_events,plot_ectopic,plot_shortlong,plot_subspaces,plot_frequencyplot_timedomain,plot_nonlinear
Examples
Visualizing HRV frequency domain from RR time series using Matplotlib as plotting backend.
from systole import import_rr from systole.plots import plot_frequency # Import PPG recording as numpy array rr = import_rr().rr.to_numpy() plot_frequency(rr, input_type="rr_ms")
<Axes: title={'center': 'Power Spectral Density'}, xlabel='Frequency [Hz]', ylabel='PSD [$s^2$/Hz]'>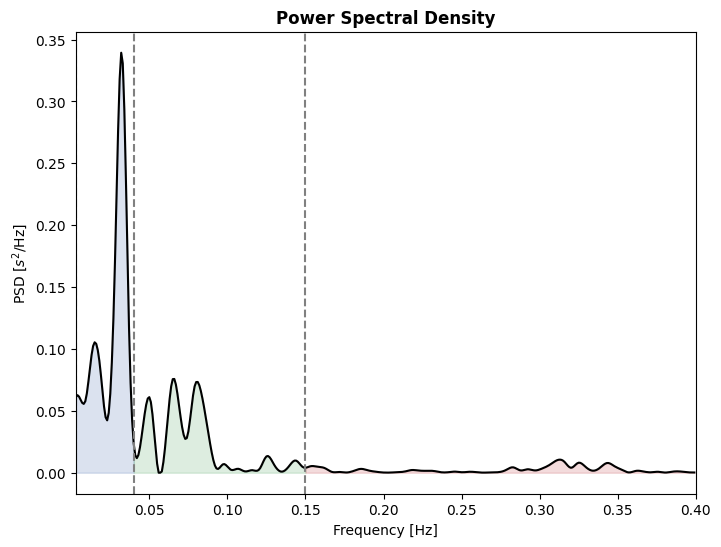
Visualizing HRV frequency domain from RR time series using Bokeh as plotting backend.